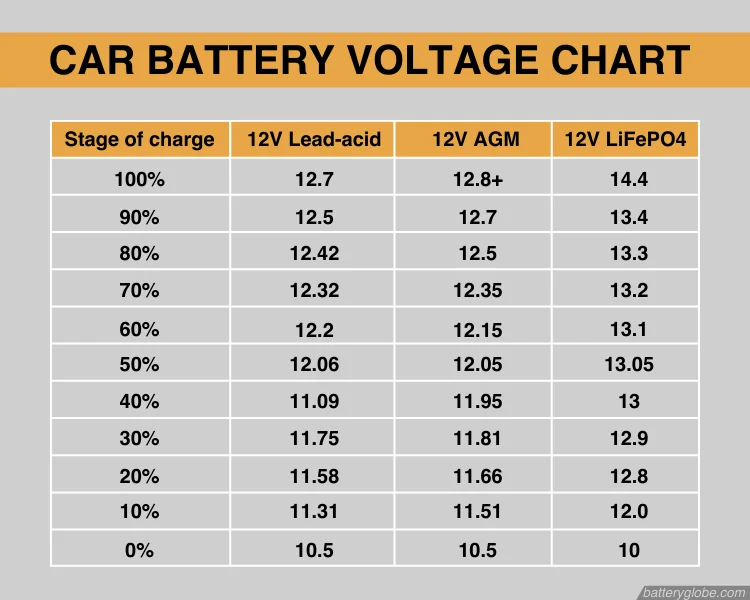
Ever been stranded with a car that just won't start? It's a terrible feeling, especially when you're running late or stuck in an inconvenient location. More often than not, the culprit is a dead or dying battery. But how do you know if your battery is the problem, and more importantly, what voltage should it have to keep your car running smoothly?
The frustration of a failing car battery can be significant. It's not just the inconvenience of being stuck; it's the uncertainty, the potential cost of repairs, and the worry that it will happen again. Understanding the basics of car battery voltage can empower you to diagnose problems early and potentially avoid those frustrating situations.
A healthy car battery should typically read between 12.6 and
12.8 volts when the engine is off. When the engine is running, this voltage should increase to between
13.7 and
14.7 volts, indicating that the charging system is working correctly. This range ensures that the battery is sufficiently charged to start the engine and power the vehicle's electrical components.
In essence, knowing the ideal voltage range for your car battery is crucial for maintaining your vehicle's reliability. A fully charged battery, around 12.6 to
12.8 volts at rest and
13.7 to
14.7 volts while the engine is running, is the key to avoiding those dreaded no-start situations and keeping your car on the road. Regularly checking your battery's voltage is a simple preventative measure that can save you time, money, and a whole lot of headaches.
Understanding Resting Voltage
Resting voltage, also known as open-circuit voltage, refers to the voltage of your car battery when the engine is off and no electrical load is being applied. This is a crucial indicator of the battery's state of charge. This relates to What Voltage Should a Car Battery Have? A Simple Guide, because it gives us a first look as to what state your battery is in.
I remember one particularly cold winter morning when my car refused to start. After several attempts, I reluctantly called a tow truck. The mechanic quickly diagnosed the problem: a dead battery. He explained that the cold weather had significantly reduced the battery's capacity, and its resting voltage was well below the acceptable level. This experience taught me the importance of regularly checking my battery's resting voltage, especially during extreme weather conditions. From that day on, I invested in a simple multimeter and made it a habit to check my battery's voltage every few months. I learned that a healthy resting voltage is typically between 12.6 and
12.8 volts. Anything below
12.4 volts indicates that the battery is discharged and needs to be recharged. A voltage below
12.0 volts suggests that the battery is severely discharged and may have suffered permanent damage.
Resting voltage is a direct reflection of the chemical reactions happening inside the battery. When a battery is fully charged, the chemical reactions are at their peak, resulting in a higher voltage. As the battery discharges, these reactions slow down, leading to a lower voltage. Several factors can affect resting voltage, including temperature, age of the battery, and the presence of any parasitic drains (electrical components that continue to draw power even when the engine is off). For instance, leaving a dome light on overnight or having a faulty component that continuously draws power can significantly reduce the battery's resting voltage.
To accurately measure resting voltage, it's essential to let the car sit for at least a few hours after it has been driven. This allows the battery to stabilize and provides a more accurate reading. When testing the voltage, use a multimeter and connect the red lead to the positive terminal and the black lead to the negative terminal. The displayed voltage will indicate the battery's resting voltage. Keeping track of these readings over time can help you identify potential issues before they lead to a complete battery failure, saving you from unexpected breakdowns and costly repairs.
Charging Voltage Explained
Charging voltage is the voltage present in your car's electrical system when the engine is running. It's a direct indication of how well your alternator is charging the battery. So what Voltage Should a Car Battery Have? A Simple Guide, is key, because we know what to expect from our battery.
A healthy charging voltage is typically between 13.7 and
14.7 volts. This higher voltage is necessary to replenish the energy used by the battery to start the engine and power the car's electrical components while driving. The alternator, driven by the engine, is responsible for maintaining this voltage. It converts mechanical energy into electrical energy, which is then used to charge the battery and power accessories like headlights, radio, and air conditioning. When the charging voltage is within the specified range, it ensures that the battery remains fully charged and ready for the next start.
If the charging voltage is too low, it indicates that the alternator is not producing enough power to charge the battery effectively. This can lead to a gradual discharge of the battery, eventually resulting in a no-start situation. Common causes of low charging voltage include a worn-out alternator, a loose or corroded alternator belt, or a faulty voltage regulator. On the other hand, if the charging voltage is too high, it can damage the battery by causing it to overcharge. Overcharging can lead to overheating, electrolyte loss, and ultimately, a shortened battery life. A faulty voltage regulator is often the culprit in cases of high charging voltage.
Monitoring the charging voltage is crucial for maintaining the health of your car battery and electrical system. You can easily check the charging voltage using a multimeter while the engine is running. If you notice that the voltage is consistently outside the 13.7 to
14.7 volt range, it's essential to have your charging system inspected by a qualified mechanic. Addressing charging voltage issues promptly can prevent more significant problems down the road, saving you from costly repairs and unexpected breakdowns. Regular monitoring and maintenance of your charging system will ensure that your battery remains in optimal condition and your car starts reliably every time.
Historical Context and Myths
The development of the car battery and understanding its voltage requirements have a rich history, filled with both scientific advancements and common misconceptions. The evolution of battery technology has been critical to the development of automobiles. Knowing What Voltage Should a Car Battery Have? A Simple Guide, keeps us on track as we look at history.
The first practical lead-acid battery, the type used in most cars today, was invented by French physicist Gaston Planté in 1859. This invention paved the way for electric vehicles and, later, internal combustion engine vehicles that relied on batteries for starting and electrical power. Early car batteries were relatively simple and unreliable, often requiring frequent maintenance and replacement. Over time, advancements in materials and manufacturing processes have led to more durable and efficient batteries.
One common myth about car batteries is that they are simply energy storage devices. While they do store electrical energy, they also play a crucial role in stabilizing the vehicle's electrical system. The battery acts as a buffer, smoothing out voltage fluctuations and protecting sensitive electronic components from damage. Another misconception is that a car battery will last indefinitely if properly maintained. While good maintenance can extend battery life, all batteries eventually degrade and need to be replaced. Factors such as temperature, vibration, and usage patterns can all affect battery lifespan.
Furthermore, there's a myth that jump-starting a car with a dead battery is always a safe and effective solution. While jump-starting can often get you back on the road, it can also damage the electrical systems of both vehicles if not done correctly. It's essential to follow the proper procedure and use jumper cables with sufficient capacity to avoid any potential harm. Understanding the historical context of car battery technology and debunking common myths can help car owners make informed decisions about battery maintenance and replacement, ensuring their vehicles remain reliable and safe.
Hidden Secrets of Car Battery Voltage
Beyond the basic understanding of resting and charging voltages, there are some lesser-known aspects that can significantly impact your car battery's health and performance. The subtle nuances in voltage readings can reveal a wealth of information about the condition of your battery and charging system. So how does What Voltage Should a Car Battery Have? A Simple Guide, apply here?
One hidden secret is the concept of "surface charge." After a battery has been charged, either by the alternator or an external charger, it can exhibit a slightly higher voltage than its true state of charge. This surface charge can mask underlying issues, such as sulfation or internal damage. To get an accurate reading of the battery's true voltage, it's essential to remove the surface charge by applying a load to the battery for a few minutes before testing. This can be done by turning on the headlights or running the blower motor for a short period.
Another secret is the impact of temperature on battery voltage. Cold weather can significantly reduce a battery's capacity and voltage output. In freezing temperatures, a fully charged battery may only deliver a fraction of its rated capacity. Conversely, hot weather can accelerate battery degradation and shorten its lifespan. Therefore, it's crucial to consider the ambient temperature when interpreting voltage readings. A battery that reads within the acceptable range on a warm day may be significantly weaker on a cold day.
Furthermore, the type of battery (e.g., flooded lead-acid, AGM, or gel cell) can influence its voltage characteristics. Different battery types have different charging requirements and voltage ranges. Using the wrong charging profile or voltage settings can damage the battery and reduce its performance. Understanding these hidden secrets can empower you to diagnose battery problems more accurately and extend the life of your car battery. By paying attention to these details, you can ensure that your battery is always in optimal condition and ready to deliver reliable starting power.
Recommendations for Maintaining Optimal Voltage
Maintaining your car battery's optimal voltage is essential for ensuring reliable starting and preventing unexpected breakdowns. Simple preventative measures can go a long way in extending your battery's lifespan and keeping your car running smoothly. The idea of What Voltage Should a Car Battery Have? A Simple Guide, helps with optimal voltage.
One key recommendation is to regularly check your battery's voltage. As mentioned earlier, both resting and charging voltages should be within the specified ranges. A simple multimeter can be used to perform these checks. Aim to check the resting voltage at least once a month and the charging voltage whenever you perform routine maintenance on your car. This will help you catch any potential issues early on before they lead to more significant problems.
Another crucial recommendation is to minimize parasitic drains. Many modern cars have electronic components that continue to draw power even when the engine is off. These parasitic drains can gradually discharge the battery over time, especially if the car is not driven frequently. To minimize these drains, make sure to turn off all lights and accessories when you exit the vehicle. If you plan to leave your car parked for an extended period, consider using a battery maintainer or disconnecting the battery altogether.
Additionally, ensure that your battery terminals are clean and free of corrosion. Corrosion can impede the flow of electricity and reduce the battery's performance. Regularly clean the terminals with a wire brush and a solution of baking soda and water. Apply a thin layer of petroleum jelly to protect the terminals from future corrosion. By following these recommendations, you can significantly extend the life of your car battery and avoid the inconvenience of a dead battery.
Factors Affecting Battery Voltage
Several factors can influence your car battery's voltage, some of which are within your control, while others are environmental. Understanding these factors can help you better manage your battery's health and prolong its lifespan. Voltage as outlined in What Voltage Should a Car Battery Have? A Simple Guide, is directly affected by factors such as:
Temperature plays a significant role in battery performance. Extreme cold can reduce a battery's capacity, making it harder to start the engine. Heat, on the other hand, can accelerate battery degradation and shorten its lifespan. Parking your car in a garage or shaded area can help mitigate the effects of extreme temperatures. If you live in a cold climate, consider using a battery blanket or trickle charger to keep the battery warm.
Another factor is the age of the battery. Car batteries typically last between three to five years, depending on usage and environmental conditions. As a battery ages, its internal resistance increases, reducing its ability to hold a charge. If your battery is approaching the end of its expected lifespan, it's a good idea to have it tested regularly and consider replacing it proactively.
Usage patterns also affect battery voltage. Frequent short trips can prevent the battery from fully charging, leading to a gradual discharge. If you primarily use your car for short trips, consider taking it for a longer drive periodically to allow the alternator to fully recharge the battery. By being mindful of these factors, you can take steps to minimize their impact on your battery's voltage and ensure its long-term health.
Essential Tips for Extending Battery Life
Extending the life of your car battery not only saves you money but also ensures your vehicle's reliability. There are several simple yet effective tips that can help you maximize your battery's lifespan. So how can What Voltage Should a Car Battery Have? A Simple Guide, help extend the battery life?
One of the most crucial tips is to avoid leaving electronic devices plugged in when the engine is off. Even when not in use, these devices can draw power from the battery, leading to a gradual discharge. Make sure to unplug your phone charger, GPS device, and other accessories before turning off the engine. Additionally, avoid leaving the headlights or interior lights on, as these can quickly drain the battery.
Another essential tip is to keep the battery terminals clean and corrosion-free. Corrosion can impede the flow of electricity and reduce the battery's performance. Regularly clean the terminals with a wire brush and a solution of baking soda and water. Apply a thin layer of petroleum jelly to protect the terminals from future corrosion. This simple maintenance task can significantly improve your battery's performance and lifespan.
Furthermore, consider investing in a battery maintainer, especially if you don't drive your car frequently. A battery maintainer is a device that provides a low, constant charge to keep the battery fully charged and prevent sulfation. This can be particularly useful if you store your car for extended periods or if you live in a cold climate. By following these tips, you can significantly extend the life of your car battery and avoid the inconvenience of a dead battery.
Understanding Sulfation
Sulfation is a natural process that occurs in lead-acid batteries, but it can become problematic if not properly managed. Sulfation happens when lead sulfate crystals form on the battery's plates, reducing its ability to accept and deliver a charge. So what does What Voltage Should a Car Battery Have? A Simple Guide, say about sulfation?
When a battery is fully charged, the lead sulfate crystals are converted back into lead and sulfuric acid. However, if the battery is consistently undercharged or left in a discharged state, these crystals can harden and become difficult to break down. This hardened sulfation reduces the battery's capacity and can eventually lead to premature failure. Factors that contribute to sulfation include infrequent use, prolonged storage, and exposure to extreme temperatures.
To prevent sulfation, it's essential to keep your battery fully charged whenever possible. Avoid leaving your car parked for extended periods without driving it. If you plan to store your car for a long time, consider using a battery maintainer to keep the battery charged. Additionally, ensure that your charging system is working correctly and that the battery is receiving the proper voltage. Regular battery maintenance and proper charging practices can help minimize sulfation and extend the life of your car battery.
Fun Facts About Car Batteries
Car batteries are fascinating devices with a rich history and numerous interesting facts that many people are unaware of. From their invention to their modern-day applications, car batteries have played a crucial role in the automotive industry. What Voltage Should a Car Battery Have? A Simple Guide, can also be made interesting!
One fun fact is that the first electric car was invented before the first gasoline-powered car. Electric cars were popular in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, but they were eventually overshadowed by gasoline-powered vehicles due to their limited range and charging infrastructure. However, with advancements in battery technology, electric cars are making a comeback.
Another interesting fact is that car batteries are recyclable. Lead-acid batteries are one of the most recycled products in the world, with over 99% of their components being recovered and reused. Recycling car batteries not only conserves valuable resources but also prevents environmental contamination. So, when it's time to replace your car battery, be sure to recycle the old one at a designated recycling center.
Furthermore, the size and type of car battery can vary depending on the vehicle's make and model. Some cars require a larger battery with more cold-cranking amps (CCA) to start the engine in cold weather, while others can get by with a smaller battery. Consulting your owner's manual or a battery fitment guide can help you determine the correct battery for your car.
How to Test Your Car Battery Voltage
Testing your car battery voltage is a simple process that can be done with a basic multimeter. This test can help you determine the health of your battery and identify potential issues before they lead to a breakdown. But where does What Voltage Should a Car Battery Have? A Simple Guide, come in?
To test the resting voltage, first, make sure the engine is off and has been off for at least a few hours to allow the battery to stabilize. Set your multimeter to the DC voltage setting, typically around 20 volts. Connect the red lead to the positive terminal of the battery and the black lead to the negative terminal. The multimeter will display the battery's voltage. A healthy resting voltage should be between 12.6 and
12.8 volts.
To test the charging voltage, start the engine and let it idle. With the multimeter still connected to the battery terminals, observe the voltage reading. A healthy charging voltage should be between 13.7 and
14.7 volts. If the voltage is outside these ranges, it indicates a problem with the charging system, such as a faulty alternator or voltage regulator.
If you're unsure about how to perform these tests, consult your owner's manual or seek assistance from a qualified mechanic. Regular battery voltage testing can help you maintain your battery's health and prevent unexpected breakdowns.
What if Your Battery Voltage is Low?
A low battery voltage can indicate a variety of problems, ranging from a simple discharge to a more serious issue with the battery or charging system. Knowing how to respond to a low voltage reading can help you avoid getting stranded and potentially save you money on repairs. What Voltage Should a Car Battery Have? A Simple Guide, is the base for this section.
If your battery's resting voltage is below 12.4 volts, it indicates that the battery is discharged and needs to be recharged. You can try jump-starting the car using jumper cables and another vehicle. However, if the battery is severely discharged, it may not hold a charge and may need to be replaced. Alternatively, you can use a battery charger to recharge the battery. Follow the charger's instructions carefully and allow the battery to charge fully before attempting to start the car.
If the charging voltage is below 13.7 volts, it indicates that the alternator is not producing enough power to charge the battery effectively. This could be due to a worn-out alternator, a loose or corroded alternator belt, or a faulty voltage regulator. In this case, it's essential to have your charging system inspected by a qualified mechanic. Ignoring a low charging voltage can lead to a gradual discharge of the battery and eventually a no-start situation.
In some cases, a low battery voltage may be caused by a parasitic drain, such as a faulty component that continues to draw power even when the engine is off. To identify a parasitic drain, you can use a multimeter to measure the current draw with the engine off. Consult a qualified mechanic for assistance in diagnosing and resolving parasitic drain issues.
Listicle: 5 Signs of a Failing Car Battery
Recognizing the signs of a failing car battery can help you take proactive steps to avoid getting stranded. Here are five common signs to watch out for. The key is knowing What Voltage Should a Car Battery Have? A Simple Guide, which leads us to recognizing problems.
- Slow Engine Crank: If your engine cranks slowly or hesitates when you try to start the car, it could be a sign that the battery is losing its ability to deliver sufficient power.
- Dim Headlights: Dim or flickering headlights, especially at idle, can indicate that the battery is not providing enough voltage to power the car's electrical system.
- Check Engine Light: The check engine light can illuminate for a variety of reasons, including a low battery voltage. Have your car scanned for codes to determine the cause.
- Swollen Battery Case: A swollen or bulging battery case is a sign of internal damage and can indicate that the battery is nearing the end of its life.
- Corrosion on Battery Terminals: Corrosion on the battery terminals can impede the flow of electricity and reduce the battery's performance. Clean the terminals regularly to prevent this issue.
Question and Answer
Here are some frequently asked questions about car battery voltage:
Q: What is the ideal voltage for a car battery?
A: A healthy car battery should have a resting voltage between 12.6 and
12.8 volts and a charging voltage between
13.7 and
14.7 volts.
Q: How often should I check my car battery voltage?
A: It's a good idea to check your battery voltage at least once a month or whenever you perform routine maintenance on your car.
Q: Can a dead battery damage my car?
A: Yes, a dead battery can potentially damage your car's electrical system if not addressed promptly. It's best to have the battery recharged or replaced as soon as possible.
Q: What should I do if my car battery keeps dying?
A: If your car battery keeps dying, it could indicate a problem with the charging system or a parasitic drain. Have your car inspected by a qualified mechanic to diagnose and resolve the issue.
Conclusion of What Voltage Should a Car Battery Have? A Simple Guide
Understanding the proper voltage range for your car battery is essential for maintaining your vehicle's reliability and preventing unexpected breakdowns. By regularly checking your battery's resting and charging voltages, you can identify potential issues early on and take proactive steps to address them. Remember, a healthy battery is a happy battery, and a happy battery means a reliable car that gets you where you need to go.