Picture this: you're all set for a weekend adventure, you turn the key in your car, and... nothing. That sinking feeling when your battery is dead. Knowing how to properly charge a 12V battery can save you from frustrating situations and extend the life of your battery, saving you money in the long run.
Let's face it, dealing with a dead battery is a hassle. It throws a wrench into your plans, leaving you stranded and searching for help. Understanding the proper charging methods, safety precautions, and the right tools can feel overwhelming, especially if you're not a car enthusiast. The fear of damaging your battery or even causing an accident is a real concern for many.
This guide will walk you through everything you need to know about charging a 12V battery safely and effectively. We'll cover the necessary tools, step-by-step instructions, crucial safety tips, and even some troubleshooting advice. Whether you're dealing with a car battery, a marine battery, or a battery for your RV, this comprehensive guide has you covered.
In summary, we've covered the essential tools, a step-by-step guide, vital safety tips, troubleshooting, and best practices for charging your 12V battery. You now have the knowledge to confidently and safely keep your batteries in top condition. By understanding the nuances of charging, you can avoid frustrating breakdowns, extend battery life, and ultimately save money. Keep in mind the importance of proper ventilation, using the correct charger type, and regularly checking your battery's condition. Applying this knowledge will keep your 12V battery in tip-top shape.
Choosing the Right Charger
Picking the right charger can feel like navigating a minefield. I remember the first time I tried charging my boat battery – I grabbed the old trickle charger my dad used for his lawnmower. Big mistake! It took forever, and I'm pretty sure I didn't even get a full charge. Choosing the right charger depends on the type of battery you're charging (lead-acid, AGM, gel cell, lithium-ion) and its capacity (measured in amp-hours). Overcharging a battery can damage it, while undercharging can shorten its lifespan. For lead-acid batteries, a smart charger with automatic shut-off is a great option. It will monitor the battery's voltage and adjust the charging current accordingly, preventing overcharging. If you have an AGM or gel cell battery, make sure the charger is compatible with these types of batteries, as they require specific charging profiles. Lithium-ion batteries need a charger specifically designed for them; using the wrong charger can be dangerous. Remember to always check the battery manufacturer's recommendations for the correct charging voltage and current.
Step-by-Step Charging Guide
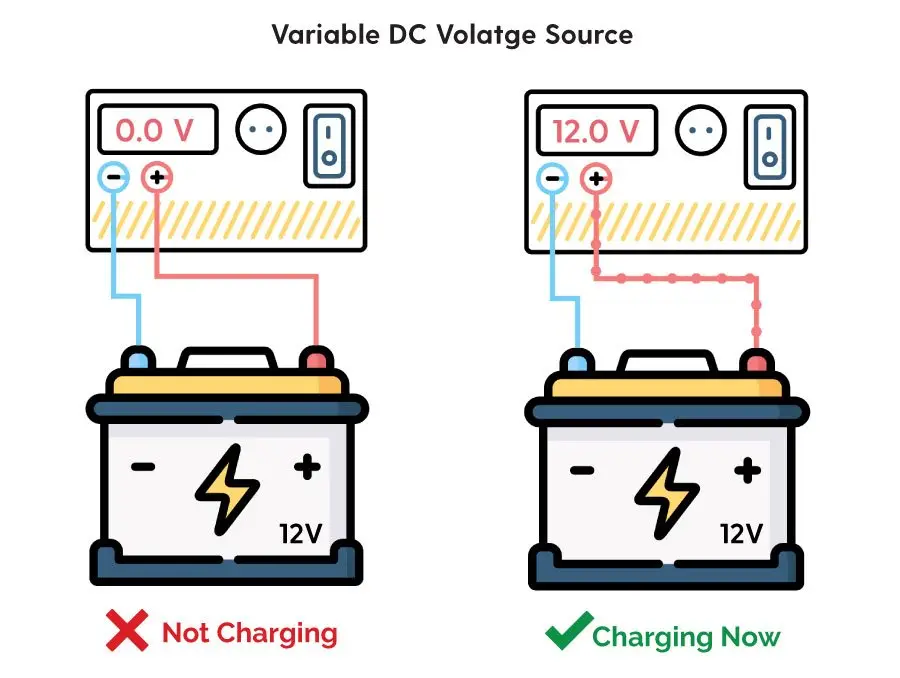
Charging a 12V battery might seem daunting, but it's actually a straightforward process when broken down into simple steps. First, gather your tools: a battery charger, safety glasses, and gloves. Make sure the area is well-ventilated to prevent the buildup of explosive gases. Disconnect the battery from the vehicle by removing the negative terminal first, then the positive. This prevents accidental short circuits. Clean the battery terminals with a wire brush to remove any corrosion, which can impede charging. Connect the charger to the battery, making sure to match the polarity: positive to positive, negative to negative. Set the charger to the correct voltage and amperage settings according to the battery manufacturer's recommendations. Turn on the charger and let it run until the battery is fully charged. This can take several hours, depending on the battery's condition and the charger's output. Once charged, turn off the charger and disconnect it from the battery. Reconnect the battery to the vehicle, positive terminal first, then negative. Ensure the terminals are securely tightened.
The History and Evolution of Battery Charging
The history of battery charging is intertwined with the development of batteries themselves. The earliest batteries, like Alessandro Volta's voltaic pile in the 1800s, were primary batteries, meaning they couldn't be recharged. The invention of the lead-acid battery by Gaston Planté in 1859 marked a turning point, as it was the first rechargeable battery. Early charging methods were rudimentary, often involving a simple connection to a DC power source. As technology advanced, more sophisticated charging circuits were developed to control the charging voltage and current. In the mid-20th century, trickle chargers became popular for maintaining battery charge over long periods. Today, smart chargers with microprocessors and advanced algorithms offer precise control over the charging process, optimizing battery performance and lifespan. The evolution of battery charging continues with the development of new charging technologies for lithium-ion and other advanced battery chemistries, driven by the growing demand for electric vehicles and portable electronics.
Unlocking Hidden Secrets of Battery Longevity
While proper charging is crucial, there are hidden secrets to maximizing battery longevity that go beyond the basics. One key factor is temperature. Extreme heat or cold can significantly reduce battery performance and lifespan. Avoid storing batteries in direct sunlight or in extremely cold environments. Another secret is to avoid deep discharges whenever possible. Regularly discharging a battery to very low levels can cause irreversible damage. Instead, try to keep the battery charged above 20% of its capacity. Sulfation, the buildup of lead sulfate crystals on the battery plates, is a common cause of battery failure. Using a desulfating charger periodically can help prevent or reverse sulfation. Finally, regularly inspect your battery for signs of damage, such as cracks, leaks, or bulging. Addressing these issues early can prevent more serious problems down the road.
Expert Recommendations for Battery Maintenance
Maintaining your 12V battery properly can significantly extend its lifespan and save you money in the long run. Experts recommend investing in a high-quality smart charger with automatic shut-off to prevent overcharging. Use a battery maintainer during periods of inactivity to keep the battery at its optimal charge level. Periodically check the battery's voltage with a multimeter to ensure it's within the recommended range. Clean the battery terminals regularly with a wire brush and apply a corrosion inhibitor to prevent buildup. If you live in a cold climate, consider using a battery warmer to keep the battery at a suitable temperature. When replacing a battery, always choose a battery with the correct specifications for your vehicle or application. Finally, dispose of old batteries properly by taking them to a recycling center or auto parts store.
Understanding Battery Chemistry: Lead-Acid, AGM, and Lithium-Ion
The world of 12V batteries encompasses several different chemistries, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Lead-acid batteries, the most common type, are relatively inexpensive and widely available. They come in two main types: flooded and sealed. Flooded lead-acid batteries require periodic maintenance to check and replenish the electrolyte level, while sealed lead-acid batteries, such as AGM (Absorbent Glass Mat) batteries, are maintenance-free and spill-proof. AGM batteries also offer better performance in cold weather and can withstand more vibration than flooded batteries. Lithium-ion batteries are the newest and most advanced type of 12V battery. They offer several advantages over lead-acid batteries, including lighter weight, higher energy density, and longer lifespan. However, they are also more expensive and require a specialized charger. Understanding the differences between these battery chemistries is crucial for choosing the right battery for your needs and ensuring proper charging and maintenance.
Essential Tips for Maximizing Battery Life
Extending the life of your 12V battery is all about adopting good charging habits and performing regular maintenance. Always use a charger that is compatible with your battery type and voltage. Avoid overcharging or undercharging the battery, as both can shorten its lifespan. If you're not using the battery for an extended period, store it in a cool, dry place and use a battery maintainer to keep it at its optimal charge level. Regularly inspect the battery for signs of corrosion, damage, or swelling. Clean the battery terminals with a wire brush and apply a corrosion inhibitor to prevent buildup. Check the battery's voltage periodically with a multimeter to ensure it's within the recommended range. If you notice any signs of a failing battery, such as slow cranking or dim lights, have it tested by a professional.
Safety First: Handling Batteries with Care
Working with 12V batteries involves certain risks, so it's essential to prioritize safety. Batteries contain corrosive acid and can produce explosive gases, so always wear safety glasses and gloves when handling them. Work in a well-ventilated area to prevent the buildup of hydrogen gas. Never smoke or use open flames near a battery. Disconnect the battery from the vehicle before charging to prevent accidental short circuits. When connecting the charger, make sure to match the polarity: positive to positive, negative to negative. If you spill battery acid, neutralize it with baking soda and rinse with plenty of water. If battery acid gets in your eyes, flush them immediately with water for at least 15 minutes and seek medical attention. Dispose of old batteries properly by taking them to a recycling center or auto parts store.
Fun Facts About Batteries
Did you know that the world's smallest battery is about the size of a grain of rice? Or that the largest battery is used to power submarines? Batteries have come a long way since Alessandro Volta invented the first battery in 1800. The term "battery" originally referred to a series of similar objects grouped together, like a battery of cannons. The first rechargeable battery was the lead-acid battery, invented in
1859. Today, batteries power everything from our smartphones to our cars to our homes. The development of new battery technologies is crucial for the transition to a more sustainable energy future. Scientists are constantly working on improving battery performance, safety, and cost.
How to Choose the Right Battery for Your Needs
Selecting the right 12V battery for your specific application is crucial for optimal performance and longevity. Consider the following factors: battery type (lead-acid, AGM, lithium-ion), capacity (measured in amp-hours), cold cranking amps (CCA), reserve capacity (RC), and physical size. For automotive applications, choose a battery that meets or exceeds the vehicle manufacturer's specifications for CCA and RC. For marine or RV applications, consider the battery's deep cycle capability, which refers to its ability to withstand repeated discharges and recharges. If weight is a concern, lithium-ion batteries offer a significant advantage over lead-acid batteries. Also, consider the battery's warranty and reputation for reliability. Reading online reviews and consulting with a battery specialist can help you make an informed decision.
What Happens If You Overcharge a 12V Battery?
Overcharging a 12V battery can have serious consequences, leading to reduced battery life, damage, and even safety hazards. When a battery is overcharged, the electrolyte solution can break down, producing hydrogen and oxygen gases. This can cause the battery to swell, leak, or even explode. Overcharging can also damage the battery plates, reducing its capacity and lifespan. In lead-acid batteries, overcharging can lead to sulfation, the buildup of lead sulfate crystals on the plates. In lithium-ion batteries, overcharging can cause thermal runaway, a dangerous condition that can lead to fire or explosion. To prevent overcharging, always use a charger with automatic shut-off and follow the battery manufacturer's recommendations for charging voltage and current. Regularly monitor the battery's voltage and temperature during charging. If you notice any signs of overcharging, such as swelling, leaking, or excessive heat, disconnect the charger immediately.
Top 5 Mistakes to Avoid When Charging a 12V Battery
Charging a 12V battery might seem simple, but there are several common mistakes that can damage the battery or create safety hazards. Here are the top 5 mistakes to avoid: 1. Using the wrong charger: Always use a charger that is compatible with your battery type and voltage.
2. Overcharging the battery: Overcharging can lead to damage, swelling, and even explosion. Use a charger with automatic shut-off.
3. Charging in a poorly ventilated area: Batteries produce explosive gases during charging, so work in a well-ventilated area.
4. Neglecting to clean the battery terminals: Corrosion on the terminals can impede charging and reduce battery performance.
5. Ignoring safety precautions: Always wear safety glasses and gloves when handling batteries to protect yourself from corrosive acid and potential explosions.
Question and Answer About How to Charge a 12V Battery
Q: How often should I charge my 12V battery?
A: It depends on how often you use the battery and its state of charge. If you use the battery regularly, charge it whenever it drops below 50% of its capacity. If you store the battery for extended periods, use a battery maintainer to keep it at its optimal charge level.
Q: Can I use a car charger to charge a marine battery?
A: It depends on the charger and the battery type. Some car chargers have settings for different battery types, including marine batteries. However, it's always best to use a charger specifically designed for the type of battery you're charging.
Q: How long does it take to charge a 12V battery?
A: The charging time depends on the battery's capacity, the charger's output, and the battery's state of charge. A fully discharged battery can take several hours to charge completely.
Q: What should I do if my battery won't charge?
A: First, check the battery terminals for corrosion and clean them with a wire brush. Make sure the charger is properly connected and set to the correct voltage and amperage. If the battery still won't charge, it may be damaged or sulfated and need to be replaced.
Conclusion of How to Charge a 12V Battery
Mastering the art of charging a 12V battery isn't just about convenience; it's about prolonging the life of your battery, ensuring your equipment is always ready when you need it, and, most importantly, doing so safely. By following the guidelines we've discussed – choosing the right charger, understanding the different battery types, prioritizing safety, and adopting smart maintenance habits – you'll be well-equipped to handle any battery charging situation. Remember to always refer to your battery manufacturer's recommendations for specific charging instructions. With the right knowledge and practices, you can keep your 12V batteries in optimal condition for years to come.