Ever been stranded with a car that justwon'tstart? That sinking feeling when you turn the key and hear nothing but a click (or worse, silence) can be incredibly frustrating. More often than not, the culprit is hiding right under the hood: your car battery.
Figuring out why your car battery isn't cooperating can feel like deciphering a secret code. Is it completely dead? Is it just low? Are there deeper problems at play? And what do all those numbers on the battery itself evenmean? It's enough to make anyone's head spin.
This guide is here to demystify the world of car battery voltage. We'll break down what those numbers actually signify, what to expect at different voltage levels (from a concerning 7V to a healthy 14V), and what you can do to keep your car battery in tip-top shape. Get ready to learn everything you need to know about your car's power source!
Understanding car battery voltage is key to preventing unexpected breakdowns. We'll cover the ideal voltage range, what different voltage levels indicate about your battery's health, and practical tips for maintaining your battery's performance. By the end of this article, you'll be empowered to troubleshoot common battery issues and extend the life of your car's most vital component. Think of it as a crash course in automotive electricity, designed to keep you moving!
My Car Battery Nightmare: A Voltage Lesson
I'll never forget the time I was driving cross-country, miles from anywhere, when my car started acting up. The lights dimmed, the radio cut out intermittently, and the engine felt sluggish. Panic started to set in. Was it the alternator? The fuel pump? I pulled over, popped the hood, and stared blankly at the battery. I knewsomethingwas wrong, but I didn't have the knowledge to diagnose the problem. I ended up calling a tow truck (expensive!) and spending a night in a questionable motel waiting for a mechanic. He told me my battery was severely discharged and likely on its last legs. If I had understood battery voltage then, I might have been able to catch the problem before it left me stranded.
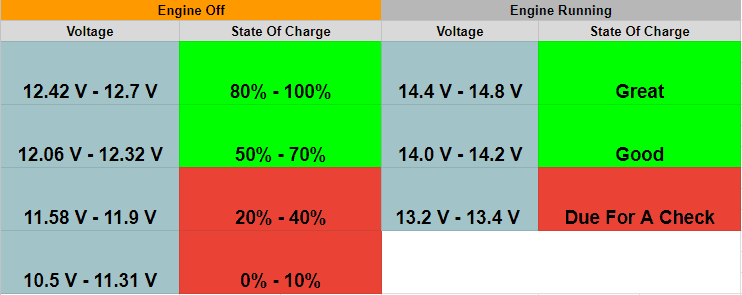
A healthy car battery typically hovers around 12.6 volts when the engine is off. This is a good baseline to remember. When the engine is running and the alternator is doing its job, you should see a reading between
13.7 and
14.7 volts. Anything significantly lower or higher indicates a problem. A reading of
12.4 volts indicates your battery is about 75% charged. A reading of
12.2 volts means only 50% charged. When the reading is
11.9 volts, your battery is considered fully discharged.
If you see a voltage reading below 12 volts when the engine is off, it's a sign that your battery is losing its charge. This could be due to several factors, including leaving your lights on, a parasitic draw (something in your car constantly draining power), or simply an aging battery that's no longer holding a charge effectively. Paying attention to these voltage readings can provide valuable early warning signs, giving you time to take action before you end up stuck on the side of the road.
Understanding Car Battery Voltage: The Numbers Game
Car battery voltage, simply put, is a measure of the electrical potential stored within the battery. It’s the force that pushes electricity through your car's electrical system, powering everything from the starter motor to the headlights. Think of it like water pressure in a pipe – the higher the pressure (voltage), the stronger the flow of electricity.
A typical 12-volt car battery doesn’t actually deliver a steady 12 volts all the time. When fully charged and at rest, it should read around 12.6 volts. This is its “open circuit voltage.” When you start the car, the voltage drops as the starter motor draws a large amount of current. However, once the engine is running, the alternator takes over, recharging the battery and maintaining a voltage between
13.7 and
14.7 volts. This charging voltage is crucial for keeping the battery topped up and ensuring your car's electrical systems have enough power. Deviations from these ranges can signal problems with the battery, the alternator, or the car's electrical system itself. Low voltage can lead to starting problems, while high voltage can damage sensitive electronic components. Regularly checking your battery voltage with a multimeter is a simple but effective way to monitor its health and prevent costly repairs.
A Brief History and Some Myths About Car Battery Voltage
The history of car batteries is intertwined with the development of the automobile itself. Early cars relied on rudimentary electrical systems, but as technology advanced, so did the need for a reliable power source. The lead-acid battery, invented in the mid-19th century, quickly became the standard due to its ability to deliver high current and be recharged.
One common myth is that a car battery will last forever if properly maintained. While good maintenance can certainly extend its lifespan, all batteries eventually degrade. Factors like extreme temperatures, vibration, and repeated deep discharges can accelerate this process. Another myth is that a battery reading 12 volts is in perfect condition. As mentioned earlier, a healthy battery should read closer to 12.6 volts when at rest. A reading of 12 volts indicates a significant discharge. Furthermore, some believe that disconnecting the negative terminal is enough to prevent battery drain. While it does help, a small parasitic draw can still exist, especially in modern cars with complex electronic systems. Understanding these realities can help you make informed decisions about battery maintenance and replacement. It's also worth noting that battery technology is constantly evolving, with newer lithium-ion batteries finding their way into hybrid and electric vehicles, offering improved performance and longer lifespans compared to traditional lead-acid batteries.
The Hidden Secrets of Car Battery Voltage
Beyond the basic voltage readings, there are more subtle clues your car battery provides about its health. For instance, the rate at which the voltage drops when you start the car can be an indicator of its internal resistance. A healthy battery will maintain a relatively stable voltage during starting, while a weak battery will experience a significant drop, struggling to deliver the necessary current.
Another hidden secret lies in the battery's "surface charge." This is a temporary voltage increase that occurs immediately after charging. It can mask the true state of charge, making it seem like the battery is fully charged when it's actually not. To get an accurate reading, it's best to let the battery sit for a few hours after charging before testing its voltage. Furthermore, the specific gravity of the electrolyte in a lead-acid battery can provide insights into its condition. This requires a special tool called a hydrometer and is more common in older battery designs. Modern sealed batteries don't allow for this type of testing. Understanding these hidden secrets requires a bit more technical knowledge, but it can be invaluable for diagnosing complex battery problems and preventing unexpected failures. It's like being able to read the fine print on your battery's health report!
Recommendations for Car Battery Voltage Monitoring
Regularly monitoring your car battery voltage is a simple but effective way to prevent unexpected breakdowns. Investing in a good quality digital multimeter is a worthwhile investment for any car owner. These devices are relatively inexpensive and easy to use.
I highly recommend checking your battery voltage at least once a month, especially during extreme weather conditions. Heat and cold can both take a toll on battery performance. Pay close attention to the voltage readings before starting the car and while the engine is running. If you notice any significant deviations from the normal ranges (12.6 volts at rest,
13.7-14.7 volts while charging), it's time to investigate further. You can also take your car to a reputable auto parts store or mechanic for a free battery test. These tests often use specialized equipment to assess the battery's overall health and capacity. In addition to voltage checks, keep an eye out for other signs of a failing battery, such as slow cranking, dim headlights, and a swollen battery case. Proactive monitoring can save you time, money, and the frustration of being stranded with a dead battery. It's like having a health checkup for your car's most vital organ!
Understanding Parasitic Draw
Parasitic draw refers to the small amount of current that some components in your car continue to draw even when the ignition is turned off. Modern cars have a lot of electronic systems, such as alarm systems, clocks, and computers, that require a constant power supply to maintain their settings and functions. While this draw is usually minimal, excessive parasitic drain can deplete your battery over time, especially if the car is left unused for extended periods.
Identifying a parasitic draw can be a bit tricky, but it's a process that involves systematically disconnecting fuses and relays to isolate the circuit responsible for the drain. You'll need a multimeter set to measure amperage and a basic understanding of your car's electrical system. The typical acceptable parasitic draw is usually less than 50 milliamps (0.05 amps). Anything significantly higher indicates a problem. Common culprits include faulty relays, aftermarket accessories (like poorly installed stereos or alarms), and damaged wiring. If you suspect a parasitic draw, it's best to consult with a qualified mechanic to diagnose and repair the issue. Ignoring it can lead to chronic battery drain and premature battery failure. Think of it as a slow leak in your car's electrical system – it might not be immediately apparent, but it can eventually empty the tank.
Pro Tips for Extending Car Battery Life
Extending the life of your car battery is all about minimizing stress and maximizing its charging efficiency. Here are some practical tips to keep your battery in good shape:
First, avoid short trips whenever possible. Starting your car requires a significant amount of current from the battery. Short trips don't give the alternator enough time to fully recharge the battery, leading to a gradual discharge over time. Second, turn off all accessories (lights, radio, AC) before starting the car. This reduces the load on the battery during the starting process. Third, keep the battery terminals clean and free of corrosion. Corrosion can impede the flow of electricity and reduce battery performance. A mixture of baking soda and water can be used to clean the terminals. Fourth, if you're not planning on using your car for an extended period, consider using a battery maintainer or trickle charger. These devices provide a low, continuous charge that keeps the battery topped up and prevents sulfation (a buildup of lead sulfate crystals that reduces battery capacity). Finally, protect your battery from extreme temperatures. Park in a garage or shaded area whenever possible, especially during hot weather. These simple steps can significantly extend the lifespan of your car battery and prevent unexpected starting problems. It's like giving your battery a little TLC to keep it running strong.
The Impact of Temperature on Car Battery Voltage
Temperature has a significant impact on car battery voltage and overall performance. Extreme heat can accelerate the chemical reactions within the battery, leading to increased self-discharge and corrosion. Cold temperatures, on the other hand, can slow down the chemical reactions, reducing the battery's ability to deliver current. This is why cars often struggle to start in cold weather.
Ideally, car batteries perform best at moderate temperatures. During hot weather, it's crucial to protect your battery from direct sunlight and excessive heat. Parking in a shaded area or using a battery insulator can help. In cold weather, ensuring the battery is fully charged is essential for optimal starting performance. Consider using a battery blanket or maintainer to keep the battery warm. It's also worth noting that temperature fluctuations can cause the battery case to expand and contract, potentially leading to cracks or leaks over time. Regular battery inspections can help identify any signs of damage or deterioration. Understanding the impact of temperature on car battery voltage can help you take proactive steps to protect your battery and ensure reliable starting performance, regardless of the weather conditions. It's like giving your battery a seasonal checkup to keep it running smoothly.
Fun Facts About Car Battery Voltage
Did you know that the first electric cars used rechargeable batteries all the way back in the late 19th century? While gasoline-powered cars eventually dominated the market, the electric car is making a comeback, thanks to advances in battery technology.
Another fun fact: The voltage of a car battery doesn't tell the whole story. A battery can have a good voltage reading but still be unable to deliver enough current to start the car. This is because the battery's internal resistance has increased, limiting its ability to discharge effectively. That's why a load test, which measures the battery's ability to deliver current under load, is often necessary to accurately assess its condition. Furthermore, car batteries are recyclable, and most auto parts stores offer a recycling program. Recycling your old battery helps prevent environmental contamination and conserves valuable resources. Finally, the size and type of battery required for your car depends on its engine size and electrical load. Using the wrong battery can lead to poor performance and even damage to your car's electrical system. So, always refer to your owner's manual or consult with a mechanic to ensure you're using the correct battery for your vehicle. It's like choosing the right fuel for your engine – it makes a big difference in performance and longevity.
How to Test Your Car Battery Voltage
Testing your car battery voltage is a simple process that can be done with a digital multimeter. Here's how:
First, gather your supplies: a digital multimeter, safety glasses, and gloves. Safety is paramount when working with car batteries. Second, set the multimeter to the DC voltage setting, typically around 20 volts. Third, locate the positive and negative terminals on your car battery. They are usually marked with a "+" and "-" symbol, respectively. Fourth, connect the red (positive) lead of the multimeter to the positive terminal of the battery and the black (negative) lead to the negative terminal. Make sure the connections are secure. Fifth, read the voltage displayed on the multimeter. As mentioned earlier, a fully charged battery should read around 12.6 volts when at rest. Sixth, start your car and observe the voltage reading while the engine is running. The voltage should increase to between
13.7 and
14.7 volts, indicating that the alternator is charging the battery. If the voltage readings are outside these ranges, it's time to investigate further. Remember to disconnect the multimeter leads in the reverse order (black first, then red) after completing the test. Regularly testing your car battery voltage can help you identify potential problems early on and prevent unexpected breakdowns. It's like giving your battery a regular checkup to ensure it's in good health.
What If Your Car Battery Voltage is Low?
If your car battery voltage is consistently low, it's a sign that something is amiss. A low voltage can lead to various problems, including difficulty starting the car, dim headlights, and reduced performance of other electrical components.
The first step is to identify the cause of the low voltage. It could be due to a number of factors, such as a parasitic draw, a faulty alternator, or simply an aging battery that's no longer holding a charge effectively. Start by checking for any obvious signs of a parasitic draw, such as lights left on or accessories that are still running when the ignition is turned off. Next, have your alternator tested to ensure it's charging the battery properly. If the alternator is working correctly, the problem is likely with the battery itself. In this case, you may need to replace the battery. Before doing so, consider having it professionally tested to confirm that it's indeed the root cause of the problem. Ignoring a low car battery voltage can lead to further damage to your car's electrical system. It's like neglecting a minor health issue that can eventually turn into a serious problem. Proactive troubleshooting and timely repairs can prevent costly breakdowns and keep your car running smoothly.
Listicle: 5 Signs Your Car Battery is Dying
Is your car battery on its last legs? Here are five telltale signs to watch out for:
1. Slow Cranking: The engine cranks slowly or hesitates when you try to start the car. This is a common sign that the battery is struggling to deliver enough current.
- Dim Headlights: The headlights appear dimmer than usual, especially when the engine is idling. This indicates that the battery is not providing sufficient power to the electrical system.
- Clicking Sound: You hear a clicking sound when you turn the key, but the engine doesn't start. This means the battery is not providing enough power to engage the starter motor.
- Swollen Battery Case: The battery case appears swollen or bulging. This is a sign of internal damage and can be caused by overcharging or extreme temperatures.
- Electrical Issues: You experience intermittent electrical problems, such as the radio cutting out or the power windows not working properly. This can be a sign that the battery is not providing a stable power supply.
If you notice any of these signs, it's time to have your car battery tested and potentially replaced. Ignoring these warning signs can leave you stranded with a dead battery. It's like ignoring the warning lights on your dashboard – eventually, something will break down.
Question and Answer
Q: What is the ideal voltage for a car battery when the engine is off?
A: A fully charged car battery should read around 12.6 volts when the engine is off.
Q: What voltage range should I expect to see when the engine is running?
A: When the engine is running, the voltage should be between 13.7 and
14.7 volts, indicating that the alternator is charging the battery.
Q: What does it mean if my car battery voltage is below 12 volts?
A: A voltage below 12 volts indicates that the battery is significantly discharged and may need to be recharged or replaced.
Q: How often should I check my car battery voltage?
A: It's a good idea to check your car battery voltage at least once a month, especially during extreme weather conditions.
Conclusion of Car Battery Voltage: Explained
Understanding car battery voltage is essential for maintaining your vehicle and preventing unexpected breakdowns. By knowing the ideal voltage range, recognizing the signs of a failing battery, and taking proactive steps to extend its lifespan, you can ensure that your car always starts reliably. So, grab a multimeter, check your battery voltage, and keep your car running smoothly! It’s a small investment of time that can save you from a lot of headaches down the road.